01
From supplier to the factory
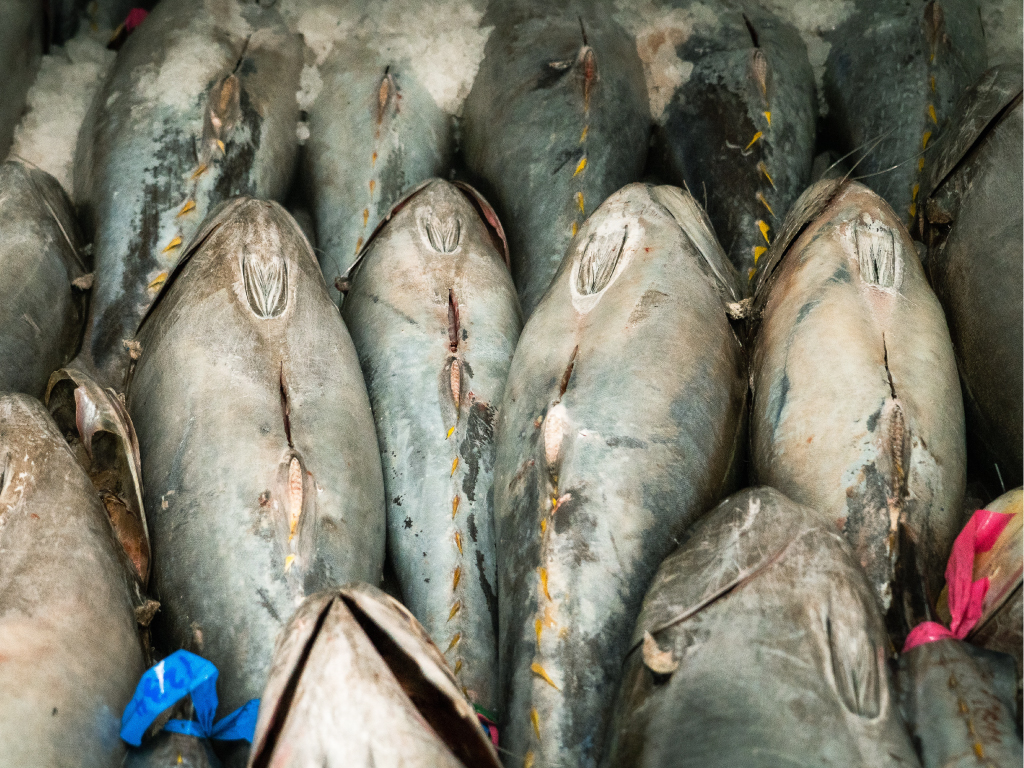
Once the fresh fish has been hauled in from the ocean, it is washed and loaded into refrigerated trucks. It is essential that all health and safety regulations are followed when unloading it from the vehicles and measuring the temperature; only fish under +4⁰C can be accepted. Additionally, a thorough inspection is done to look for signs external damage. We maintain rigorous standards, and any fish with high temperature or injury are sent back to the provider without delay.

02
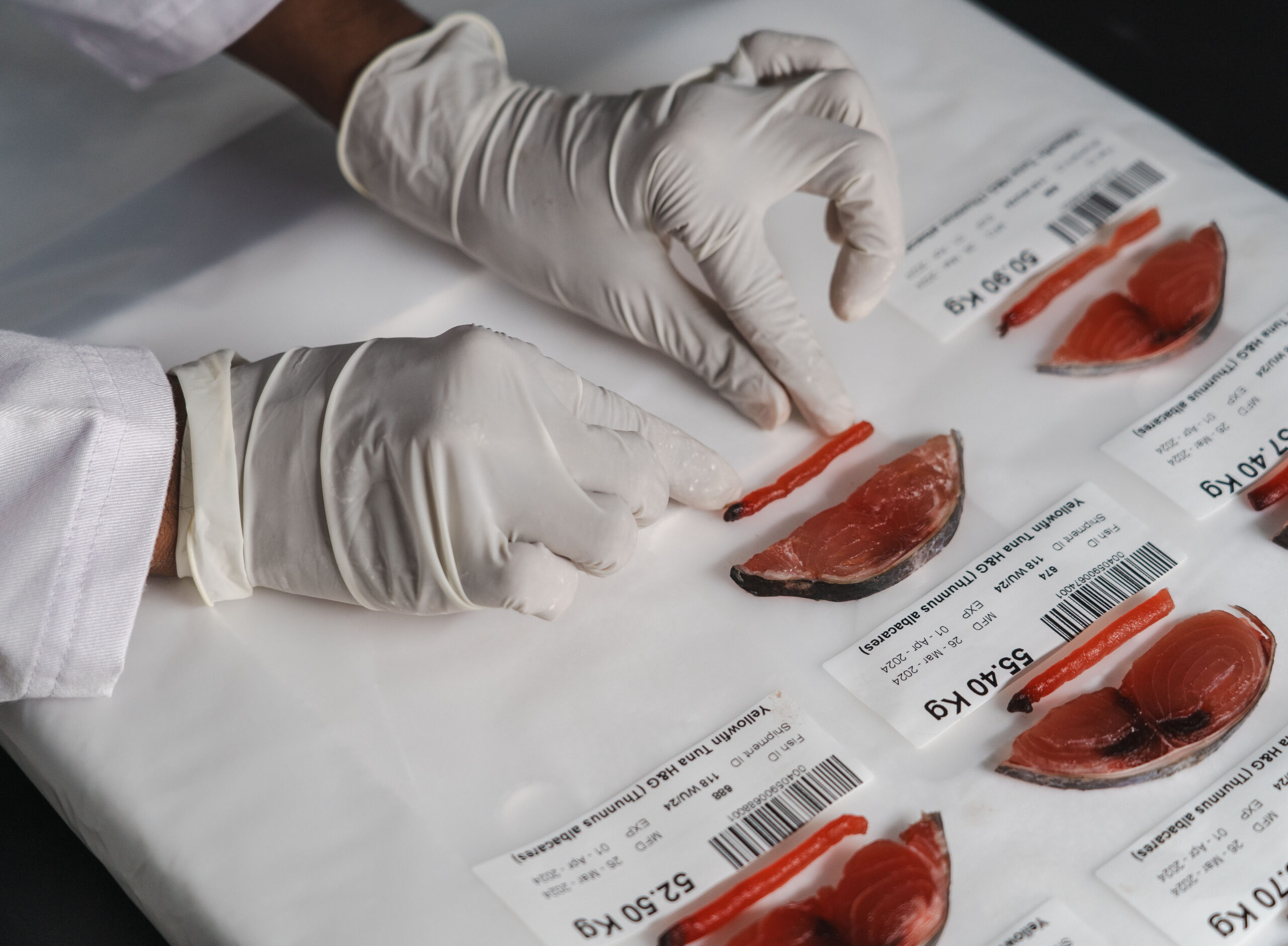
Unloading, grading and sampling
Fish that meet the required temperature standards are evaluated through a grading process. An inspector uses a clean corer to take a sample of flesh from the middle of the fish. This sample is then used to evaluate quality and classify the fish based on its color, texture, and other attributes.
03
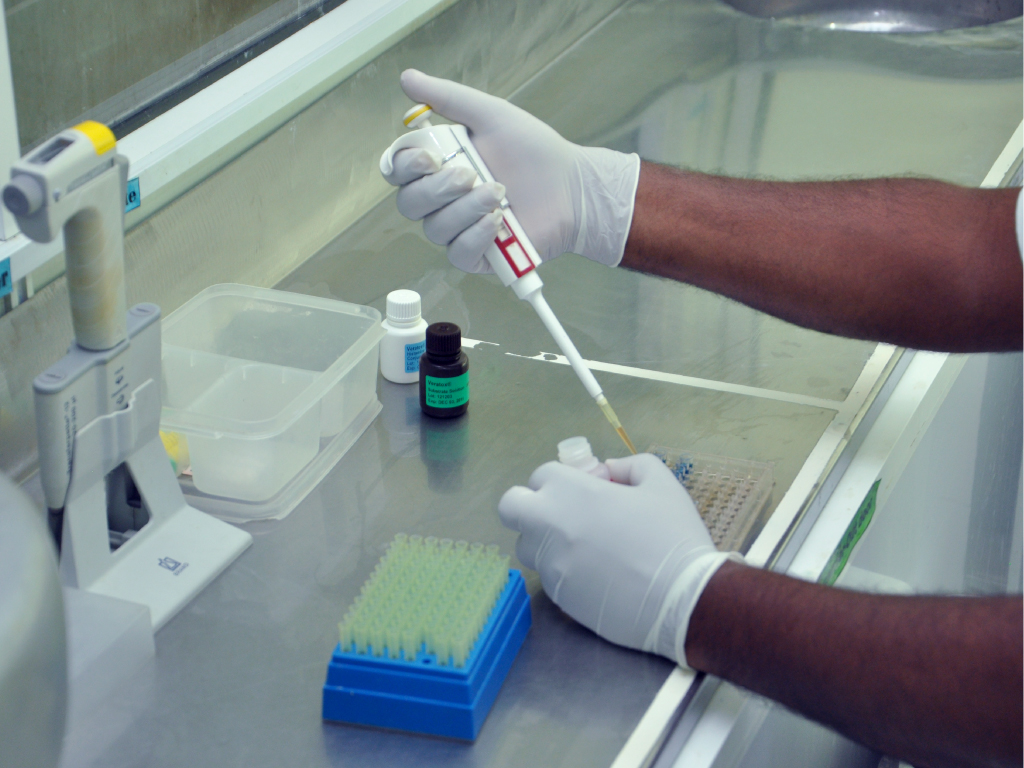
Lab testing
Once the sample has been taken, it is sent for chemical analysis in our internal laboratory. The fish are washed and carefully cleaned, and their individual weights are determined. They are stored in chill tanks until the results of their chemical tests are available. If the levels of histamine or mercury are higher than the accepted threshold, they are taken out of the chill tanks and returned to the suppliers right away. If they are within the acceptable limits, they are ready for processing.


04
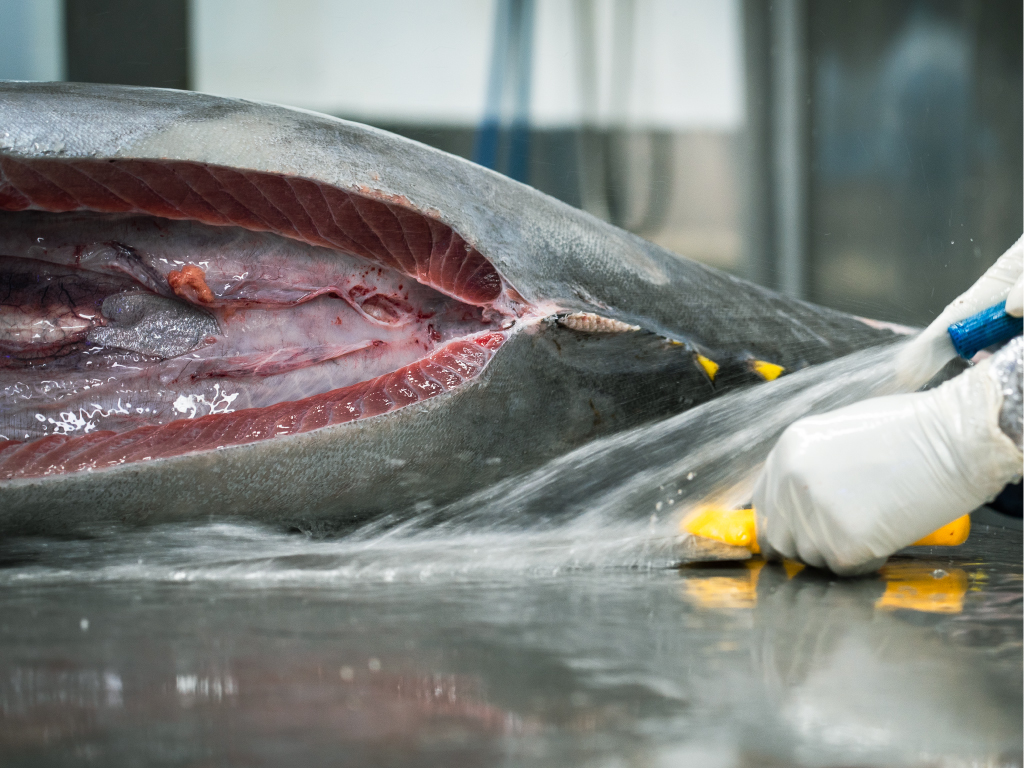
Gilling, gutting, and filleting
During the first step of processing, it is essential to remove the gills and guts of each fish. Additionally, the tails and main fins are removed while the heads are taken off in H/G shipments. Following this, each fish is scrubbed and washed. Moreover, those that require processing (except whole fish/G.G shipments) are cut into two pieces from the center bone. This is referred to as filleting, and each half is identified as a fillet. Finally, the center bone and any other bones are eliminated in the deboning procedure.
05
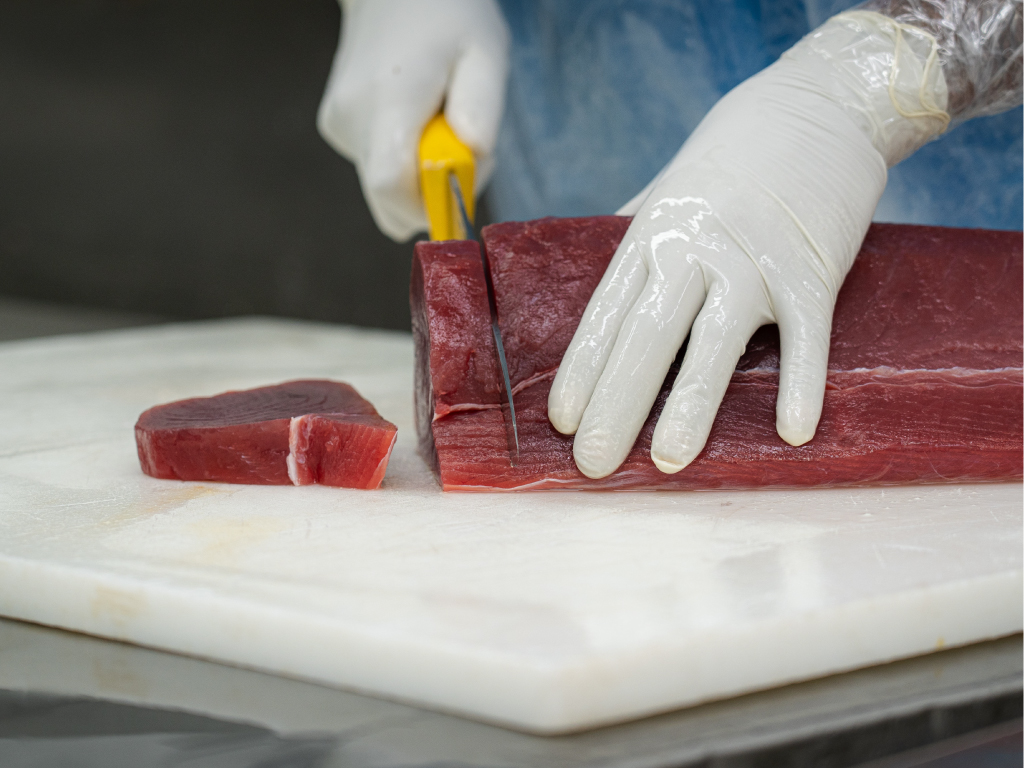
Skinning, trimming & portioning
Every fillet is divided into two sections referred to as loins. The skin, small bones, and dark meat are taken off these loins. The temperature of the loins is measured and documented. Afterwards, they are examined internally to determine if there are any cuts, bite marks, cancers, and parasitic growths. They are then processed to match the buyer’s requests such as blocks, chunks, brochettes, steaks, and saku. After the trimming and cutting, the products are wrapped to the buyer’s specifications according to the standards of seafood processing firms.


06
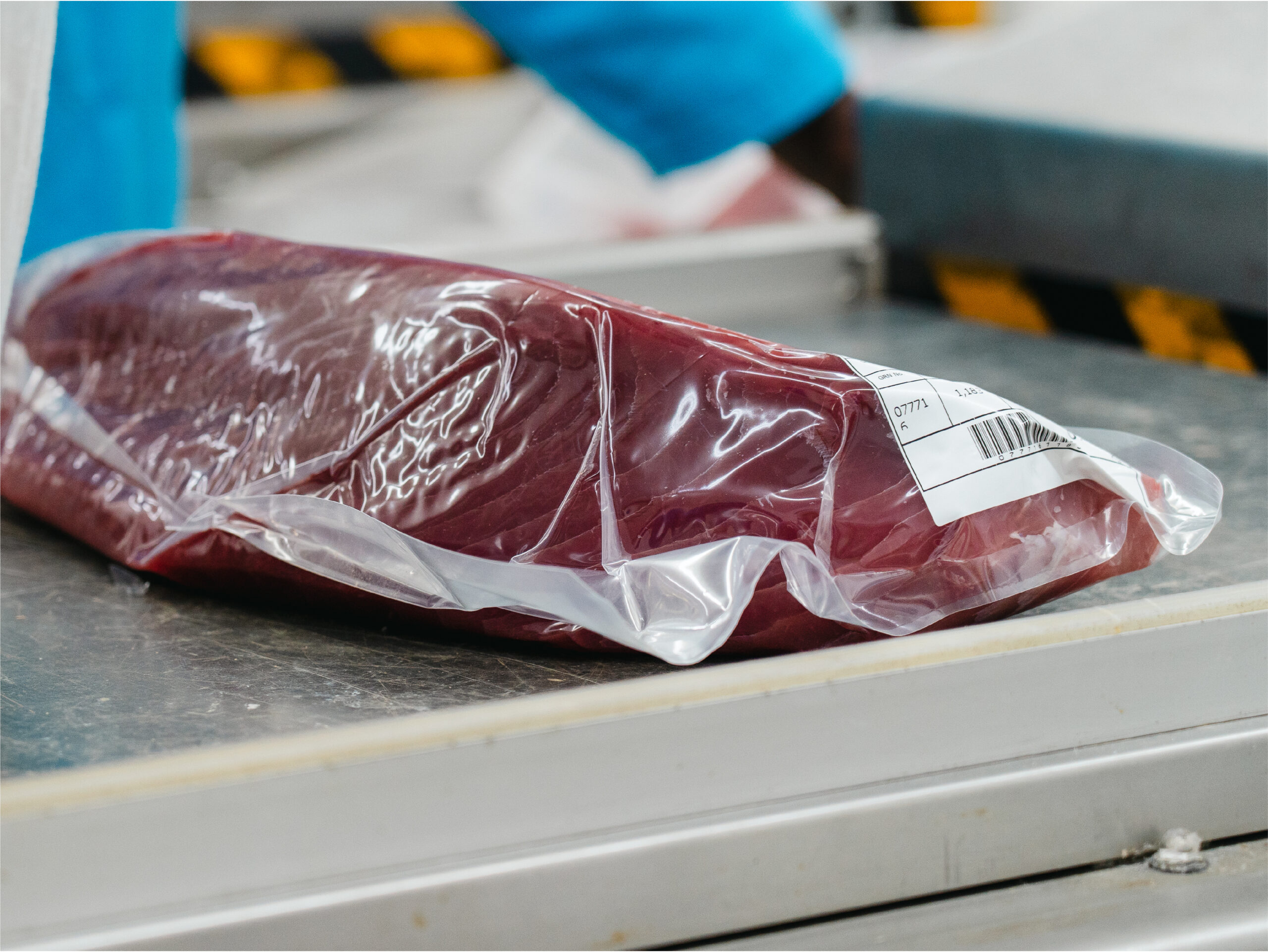
Master packing
Once the goods are finished, they are placed in vacuum-sealed bags of low-density polyethylene and nylon, and then labeled with all the product information and export requirements. Finally, all the products are vacuum-packed.
07
Dispatching
After the vacuum-sealed products are kept in ice slurries with a steady temperature of 0⁰C, they are removed and packed into rigifoam boxes or corrugated cartons with a generous amount of gel ice (dry ice can be included upon request). The box is labeled and stored within a cold room until it is ready for shipping.